AI regulation encompasses a wide range of policies, guidelines, and laws designed to oversee the development, deployment, and use of artificial intelligence technologies. The primary goals of AI regulation typically include ensuring safety, promoting ethical use, protecting privacy, and preventing bias.
Current Initiatives in AI Regulation
Globally, there have been some initiatives to regulate AI. Below are some examples.
The European Union (EU) has proposed the Artificial Intelligence Act, which classifies AI systems into different risk categories and sets requirements for each. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) also affects AI by setting strict rules on data processing and protection.
The United States of America has taken a sectoral approach, with various agencies setting guidelines for AI in specific industries. There have also been calls for more comprehensive federal AI legislation.
China has published several guidelines and regulations focusing on ethical AI use, data security, and privacy. The government also emphasises AI development as a national priority.
Bodies like the OECD and UNESCO have developed principles and recommendations for AI governance that member countries can adopt.
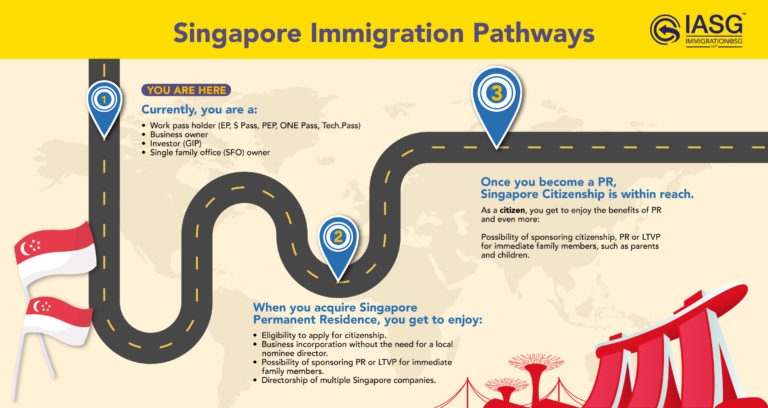
In Singapore, there are currently no specific laws that regulate AI. However, the use of AI is governed by existing sectoral laws and Singapore’s Infocomm Media Development Authority (IMDA) ensures that AI regulations undergo regular reviews to match the pace of AI development. While crimes and misuse of AI is rare, Singapore has a five-fold increase between 2022 to 2023 in the use of deepfakes. Specifically, Singapore’s Senior Minister Lee Hsien Loong became a victim of a deepfake video, making him look like he was selling an investment scheme when it is actually a scam.
Current Challenges in AI Regulation
- Balancing Innovation and Regulation: Ensuring regulations protect the public without stifling innovation.
- Global Coordination: Aligning AI regulations across different countries to manage cross-border challenges and opportunities.
- Enforcement and Adaptability: Developing effective enforcement mechanisms and ensuring regulations can adapt to rapid technological advancements.
10 Reasons for AI Regulations
AI regulation is necessary for several reasons, driven by the significant impact that artificial intelligence has on society, economies, and individual lives. As AI becomes more widespread, ensuring its responsible development and deployment is critical to mitigating risks and maximising benefits.
1. Preventing Harm and Ensuring Safety
AI systems, especially in areas like healthcare, autonomous vehicles, and financial markets, can cause significant harm if they fail. Faulty AI systems might lead to incorrect medical diagnoses, accidents with self-driving cars, or financial instability. Regulation is needed to ensure that AI systems are thoroughly tested, safe, and reliable before they are deployed in critical areas.
2. Mitigating Bias and Discrimination
AI systems can unintentionally perpetuate or amplify bias present in the data they are trained on. This can lead to discriminatory outcomes, such as biassed hiring practices, unequal access to services, or unfair treatment in law enforcement. Regulation can help by requiring AI systems to be evaluated for fairness and bias, and by setting guidelines for data use and algorithm design to minimise discrimination.
3. Protecting Privacy and Data Security
AI systems often rely on large datasets, including personal data, to function effectively. Without proper oversight, this could lead to breaches of privacy or misuse of personal information. Regulation is essential to ensure that AI respects privacy laws, like the GDPR, and uses data ethically, with proper consent and safeguards.
4. Ensuring Accountability and Transparency
AI systems can make decisions that are difficult to explain or understand, especially with complex machine learning models. This lack of transparency (often referred to as the “black box” problem) can make it difficult to hold individuals or organisations accountable when something goes wrong. Regulation can require explainability in AI systems, ensuring that their decisions can be understood, audited, and challenged when necessary.
5. Preventing the Misuse of AI
AI can be used for malicious purposes, such as deep fakes, cyberattacks, surveillance, and disinformation campaigns. These uses can harm individuals and undermine trust in public institutions. Regulation can help by setting boundaries on how AI can be used, particularly in sensitive areas like security, governance, and media. South Korea has pledged to invest US$7 million to counter deep fakes.
6. Promoting Ethical Use
AI technologies can have profound ethical implications, such as replacing human workers, determining access to critical services, or making decisions in areas like criminal justice and welfare. Ethical guidelines and regulations ensure that AI is developed and deployed in a way that respects human rights, autonomy, and dignity. Scarlett Johansson, a famous movie star, found that ChatGPT launched a voice demo that is eerily similar to hers, sparking copyright issues and debate on future works by artists being replaced by celebrities’ likeness produced by AI.
7. Economic Stability and Competition
AI has the potential to disrupt entire industries, leading to job displacement, changes in market dynamics, and economic inequality. Large companies with access to more data and resources might monopolise AI advantages, stifling competition. Regulation is needed to promote fair competition, ensure economic stability, and address potential workforce disruptions.
8. Fostering Public Trust
The public’s trust in AI is crucial for its widespread adoption. If people fear AI systems or believe they are harmful or untrustworthy, it could hinder technological progress and innovation. Regulation can build trust by ensuring that AI technologies are developed and used responsibly, with clear protections for individual rights and well-being.
9. Global Coordination and Standards
AI is a global technology, and different countries have varying approaches to its regulation. This can lead to fragmentation, where businesses and individuals face inconsistent rules across borders. International regulation helps create a level playing field, fosters collaboration, and ensures that AI development is aligned with global ethical standards.
10. Protecting Democracy and Freedom
AI technologies, such as surveillance systems and algorithms used for social media manipulation, can be used by governments or corporations to influence public opinion, limit freedom of speech, or suppress dissent. Regulation is important to protect democratic processes and individual freedoms, ensuring that AI is not used to undermine political systems or civil liberties. In August 2024, Donald Trump posted an AI generated picture of famous singer Taylor Swift supporting his political campaign.
Opportunities for Businesses
1. AI Governance Solutions
Companies can offer software or services that help businesses monitor and maintain compliance with AI regulations. These could include tools for AI auditing, bias detection, and automated compliance checks. As regulations become more complex, demand for AI governance platforms will increase, creating business opportunities for startups and established firms alike.
2. Ethical AI Consultancy
Provide consulting services to businesses that need help navigating AI regulations, ensuring compliance, or addressing ethical concerns like bias, fairness, and transparency. Firms with deep expertise in both AI technology and regulatory environments can help companies integrate AI responsibly.
3. Data Privacy and Security Solutions
Companies developing AI must ensure data protection. Startups focusing on AI-specific privacy and cybersecurity solutions, including secure data sharing, anonymization, and secure AI deployment, will see increased demand. The need for secure AI systems and compliance with stringent data protection laws provides a significant business opportunity.
4. AI Auditing Services
Specialised firms offering auditing services to evaluate AI systems for compliance, fairness, and security can serve as third-party validators. This ensures companies avoid legal risks and meet regulatory standards. As more regulations require auditing and verification, this service will become essential, especially for businesses deploying AI at scale.
5. AI Liability Insurance
Insurers can develop products to cover risks associated with the use of AI systems, such as incorrect decision-making, biassed algorithms, or data breaches. As AI use expands and regulatory risks grow, specialised insurance offerings will become a new niche market for insurers.
6. Training and Education
Businesses can offer training programs to help employees and executives understand AI regulations, compliance requirements, and best practices. This includes legal education, technical workshops, and certification programs for AI governance. As companies integrate AI, the need for educating their workforce about AI regulation and ethical use will become crucial, opening doors for educational providers.
7. Regulatory Technology (RegTech)
RegTech solutions for AI can automate regulatory reporting, risk assessments, and compliance monitoring. Companies offering AI-driven tools to streamline these processes will attract businesses needing to meet compliance with minimal overhead. With businesses facing heavy fines for non-compliance, RegTech is poised for growth, particularly as AI regulations evolve.
Foreign business owners and entrepreneurs who are interested in setting up a company in Singapore, especially in up-and-coming industries such as AI, may call/Whatsapp Immigration@SG at +65 8766 1966 or email to info@iasg.com.sg.
Emerging Trends to Watch
- Cross-Border Regulation: As AI is often used across borders, businesses that offer solutions to navigate the varying global AI regulations will have significant opportunities.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Businesses collaborating with governments on AI regulatory frameworks may gain early mover advantages in understanding and influencing regulation.
- Sector-Specific Regulation: Certain sectors like healthcare, finance, and autonomous vehicles are likely to face more stringent AI regulations, creating opportunities for niche regulatory services tailored to these industries.
AI Regulation
While AI is being rapidly invested, developed, and adopted, the industry is still in its infancy. With great potential across all sectors, jobs, businesses, and societies globally will experience a transformational change. AI regulation is therefore needed to ensure safety in all aspects for all involved.